sodium thiosulfate and iodine titration
National Library of Medicine 2. 2010 Apr;35(8):1014-7. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20100816. Nuestras mquinas expendedoras inteligentes completamente personalizadas por dentro y por fuera para su negocio y lnea de productos nicos. WebAdd 4.1 g of sodium ethanoate, 50 g of potassium iodide and 9.4 g of sodium thiosulfate. We can use this to determine the concentration of iodine in a 0. 2023-03-29. Reliability in Standardization of Iron(III) and Titanium(III) Solutions in Volumetric Analysis. Still, we should remember that their shelf life is relatively short (they should be kept tightly closed in dark brown bottles, and standardized every few weeks). and transmitted securely. 4. volumetric flask and make up to 1 dm Pour the mixture into a 1 dm 3 3 with water. Titrating iodine starch solution with sodium thiosulphate - Colour change, Redox reaction between Potassium thiocyanate and iodine. This application is used to standardize Na 2 S 2 O 3 titrant with potassium iodate (KIO 3 ). The starch solution serves as an indicator of the end of the reaction by forming a deep-blue colored starchiodine complex. When starch and iodine are both present the solution is? An Iodine-Sodium Thiosulfate Titration is a laboratory experiment used to determine the amount of iodine present in a sample. Step 3: Calculate the number of moles of oxidising agent.
100% Money Back Guarantee, It would be great to have a 15m chat to discuss a personalised plan and answer any questions. Answer: (b) 2. Sodium Thiosulfate is used as the titrant, and iodine reacts with it to produce a yellow color. The iodine formed from this reaction is titrated with thiosulfate using starch as an indicator of triiodide anion. SOLUTION A : SOLUTION OF SODIUM THIOSULFATE 0.1 mol/l In the volumetric lask: Add the sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate (weigh precisely with a margin of 0.01 g) o Add distilled water to ill up the quantity to the correct volume o Close the volumetric lask with its stopper and shake slightly until complete dissolution of sodium thiosulfate. J Neurosci Methods. The deviation of the values obtained from the average can be used to determine the accuracy of the experiment. What is the purpose of the iodine clock reaction? 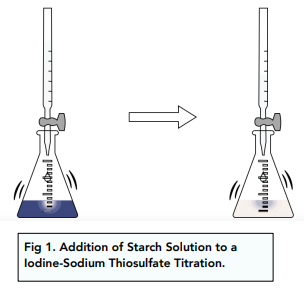 0000005738 00000 n
0000008778 00000 n
As soon as all of the S2O3 2- ions are consumed, the excess iodine produced in (5) is free to react with starch, turning the solution blue (7). 0000001027 00000 n
Small amount of carbonate added helps keep solution pH above 7, which slows down thiosulfate decomposition. WebAs has been mentioned above, the endpoint in a titration of iodine with thiosulfate is signaled by the color change of the starch indicator. It is routinely used as a titrant to determine concentrations of oxidants such as hypochlorite in bleach and dissolved oxygen in water. 1 Why is sodium thiosulfate used in iodometric titration? Webcontainer. Calculate the percentage of copper in the alloy. PK ! 0000006736 00000 n
Iodometry is one of the most important redox titration methods. The method is widely used in various industries, such as water treatment, agriculture, and food science, to monitor the levels of iodine in water, soil, and food samples.
0000005738 00000 n
0000008778 00000 n
As soon as all of the S2O3 2- ions are consumed, the excess iodine produced in (5) is free to react with starch, turning the solution blue (7). 0000001027 00000 n
Small amount of carbonate added helps keep solution pH above 7, which slows down thiosulfate decomposition. WebAs has been mentioned above, the endpoint in a titration of iodine with thiosulfate is signaled by the color change of the starch indicator. It is routinely used as a titrant to determine concentrations of oxidants such as hypochlorite in bleach and dissolved oxygen in water. 1 Why is sodium thiosulfate used in iodometric titration? Webcontainer. Calculate the percentage of copper in the alloy. PK ! 0000006736 00000 n
Iodometry is one of the most important redox titration methods. The method is widely used in various industries, such as water treatment, agriculture, and food science, to monitor the levels of iodine in water, soil, and food samples.
Commonly used solutions are 0.1M (0.1 normal).  Maquinas vending ultimo modelo, con todas las caracteristicas de vanguardia para locaciones de alta demanda y gran sentido de estetica. Accessibility Web1. WebRedox titration using sodium thiosulphate, Na2S2O3 (usually) as a reducing agent is known as iodometric titration since it is used specifically to titrate iodine. WebSo, sodium carbonate can be used either to stabilize thiosulfate, or to lower its reaction rate with anything else that it's been combined with. last modified on October 27 2022, 21:28:32. Chemistry Stack Exchange is a question and answer site for scientists, academics, teachers, and students in the field of chemistry. Webiodine solution (Section 5.4) to be titrated and dilute to 300 mL with reagent water. 0000066547 00000 n
Maquinas vending ultimo modelo, con todas las caracteristicas de vanguardia para locaciones de alta demanda y gran sentido de estetica. Accessibility Web1. WebRedox titration using sodium thiosulphate, Na2S2O3 (usually) as a reducing agent is known as iodometric titration since it is used specifically to titrate iodine. WebSo, sodium carbonate can be used either to stabilize thiosulfate, or to lower its reaction rate with anything else that it's been combined with. last modified on October 27 2022, 21:28:32. Chemistry Stack Exchange is a question and answer site for scientists, academics, teachers, and students in the field of chemistry. Webiodine solution (Section 5.4) to be titrated and dilute to 300 mL with reagent water. 0000066547 00000 n
0000009681 00000 n 2oWf [Content_Types].xml ( j0EJ(eh4NDB81$14 {1l w%=^i7+-d&0A6l4L60#S
Once the thiosulfate ion has been exhausted, this reaction stops and the blue colour caused by the triiodide starch complex appears. Additionally, the use of a standardized sodium thiosulfate solution can also improve the accuracy of the experiment. In all cases the same simple and reliable method of end point detection, based on blue starch complex, can be used. sodium thiosulfate and iodine titration. Titration Wikipedia. rev2023.4.6.43381.
In titration of iodine with sodium thiosulfate, the equivalent weight of sodium thiosulphate is ( Mol Wt 248) (a) 248 (b) 124 (c) 62 (d) 24.8. Both processes can be source of titration errors. Combining micro-computed tomography with histology to analyze biomedical implants for peripheral nerve repair. The sodium thiosulfate solution is then slowly added to the iodine solution while stirring. If it is added to a sample that contains starch, such as the bread pictured above, the color changes to a deep blue. Pick a time-slot that works best for you ? Which solution in the iodine clock reaction is regarded as the indicator? 3 How is iodine removed from the reaction mixture? 2013 Oct 15;115:258-62. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2013.04.039. Then moles of iodate = 6.60 x 10 mol / 3 = 2.20 x 10 mol. Finally, an accurate determination method for bromate was first established with high accuracy and traceability to the SI by primary methods. MeSH 4. Worked example: A student adds 25.0 cm of potassium iodate (V) solution to an excess of acidified potassium iodide solution. WebAdding sodium thiosulfate solution to the iodine solution until the blue color of the iodine starch complex disappears will indicate the endpoint of the titration. Concentration = number of moles / volume The addition of sodium thiosulfate is continued with caution drop by drop until the sample becomes water-clear. Podeli na Fejsbuku. When iodine reacts with sodium thiosulphate then it results in the formation of tetrathionate sodium and sodium iodide. 0000006757 00000 n Sodium thiosulfate solutions can be standardized by direct titration of the I 2 generated in the KIO 3 reaction using the starch-iodine complex as the indicator (remember that the iodine is actually in Could someone please tell me whether the above scenario is possible or not and why? Iodine solutions can be easily normalized against arsenic (III) oxide (As2O3) or sodium thiosulfate solution. (4 marks), Atomic Structure Electron Arrangement (A-Level Chemistry), Atomic Structure Electrons in Atoms (A-Level Chemistry), Atomic Structure Mass Spectrometry (A-Level Chemistry), Atomic Structure Element Isotopes (A-Level Chemistry), Atomic Structure Atomic and Mass Number (A-Level Chemistry), Atomic Structure Subatomic Particles (A-Level Chemistry), Equilibrium Constant for Homogenous Systems Le Chateliers Principle in Gas Equilibria (A-Level Chemistry), Equilibrium Constant for Homogenous Systems Gas Equilibria and Kp (A-Level Chemistry), Equilibrium Constant for Homogenous Systems Changing Kp (A-Level Chemistry), Equilibrium Constant for Homogenous Systems Gas Partial Pressures (A-Level Chemistry), Acids and Bases Drawing pH Curves (A-Level Chemistry), Acids and Bases Acid-Base Indicators (A-Level Chemistry), Acids and Bases Dilutions and pH (A-Level Chemistry), Electrode Potentials and Electrochemical Cells Commercial Applications of Fuel Cells (A-Level Chemistry), Electrode Potentials and Electrochemical Cells Electrochemical Cells Reactions (A-Level Chemistry), Electrode Potentials and Electrochemical Cells Representing Electrochemical Cells (A-Level Chemistry), Electrode Potentials and Electrochemical Cells Electrode Potentials (A-Level Chemistry), Electrode Potentials and Electrochemical Cells Half Cells and Full Cells (A-Level Chemistry), Acids and Bases Titrations (A-Level Chemistry), Acids and Bases Buffer Action (A-Level Chemistry), Acids and Bases pH of Strong Bases (A-Level Chemistry), Acids and Bases Ionic Product of Water (A-Level Chemistry), Acids and Bases More Ka Calculations (A-Level Chemistry), Acids and Bases The Acid Dissociation Constant, Ka (A-Level Chemistry), Acids and Bases The pH Scale and Strong Acids (A-Level Chemistry), Acids and Bases Neutralisation Reactions (A-Level Chemistry), Acids and Bases Acid and Base Strength (A-Level Chemistry), Acids and Bases The Brnsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory (A-Level Chemistry), Amount of Substance Percentage Atom Economy (A-Level Chemistry), Amount of Substance Calculating Percentage Yields (A-Level Chemistry), Amount of Substance Stoichiometric Calculations (A-Level Chemistry), Amount of Substance Balancing Chemical Equations (A-Level Chemistry), Amount of Substance Empirical and Molecular Formulae (A-Level Chemistry), Amount of Substance Further Mole Calculations (A-Level Chemistry), Amount of Substance- The Mole and The Avogadro Constant (A-Level Chemistry), Amount of Substance Measuring Relative Masses (A-Level Chemistry), Amount of Substance The Ideal Gas Equation (A-Level Chemistry), Periodicity Classification (A-Level Chemistry), Bonding Hydrogen Bonding in Water (A-Level Chemistry), Bonding Forces Between Molecules (A-Level Chemistry), Bonding Bond Polarity (A-Level Chemistry), Bonding Molecular Shapes (A-Level Chemistry), Bonding Predicting Structures (A-Level Chemistry), Bonding Carbon Allotropes (A-Level Chemistry), Bonding Properties of Metallic Bonding (A-Level Chemistry), Bonding Properties of Covalent Structures (A-Level Chemistry), Bonding Covalent Bonds (A-Level Chemistry), Kinetics The Maxwell Boltzmann Distribution and Catalysts (A-Level Chemistry), Kinetics The Collision Theory and Reaction Rates (A-Level Chemistry), Calculations with Equilibrium Constants (A-Level Chemistry), Chemical Equilibria applied to Industry (A-Level Chemistry), Chemical Equilibria and Le Chateliers Principle (A-Level Chemistry), Oxidation, Reduction and Redox Equations Balancing Redox Equations (A-Level Chemistry), Oxidation, Reduction and Redox Equations Redox Processes (A-Level Chemistry), Oxidation, Reduction and Redox Equations Oxidation States (A-Level Chemistry), Thermodynamic Calculations involving Free Energy (A-Level Chemistry), Thermodynamic Gibbs Free Energy (A-Level Chemistry), Thermodynamic Entropy Change Predictions (A-Level Chemistry), Thermodynamic Total Entropy Changes (A-Level Chemistry), Thermodynamic Introduction to Entropy (A-Level Chemistry), Thermodynamic Calculating Enthalpy Changes of Solution (A-Level Chemistry), Thermodynamic Enthalpy of Solution (A-Level Chemistry), Thermodynamic Enthalpy of Hydration (A-Level Chemistry), Thermodynamic Calculations involving Born-Haber Cycles (A-Level Chemistry), Thermodynamic Construction of Born-Haber Cycles (A-Level Chemistry), Rate Equations Reaction Determining Steps (A-Level Chemistry), Rate Equations Reaction Half Lives (A-Level Chemistry), Rate Equations Uses of Clock Reactions (A-Level Chemistry), Rate Equations Determining Orders of Reactions Graphically (A-Level Chemistry), Rate Equations Determining Order of Reaction Experimentally (A-Level Chemistry), Rate Equations Temperature Changes and the Rate Constant (A-Level Chemistry), Rate Equations The Rate Constant (A-Level Chemistry), Rate Equations Introduction to Orders of Reactions (A-Level Chemistry), Rate Equations The Rate Equation (A-Level Chemistry), Rate Equations Measuring Rate of Reaction (A-Level Chemistry), Periodicity Trends Along Period 3 (A-Level Chemistry), Uses of Group 2 Elements and their Compounds (A-Level Chemistry), Reactions of Group 2 Elements (A-Level Chemistry), Group 2, The Alkaline Earth Metals (A-Level Chemistry), The Halogens -Halide Ions and their Reactions (A-Level Chemistry), The Halogens Disproportionation Reactions in Halogens (A-Level Chemistry), The Halogens Reactions with Halogens (A-Level Chemistry), The Halogens Group 7, The Halogens (A-Level Chemistry), Properties of Period 3 Elements Properties of Period 3 Compounds (A-Level Chemistry), Properties of Period 3 Elements Reactivity of Period 3 Elements (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Autocatalysis of Transition Metals (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Transition Metals as Homogeneous Catalysts (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Transition Metals as Heterogeneous Catalysts (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Examples of Redox Reactions in Transition Metals (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Carrying Titrations with Potassium Permanganate (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Redox Titrations (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Redox Potentials (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Redox Reactions Revisited (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Ligand Substitution Reactions (A-Level Chemistry), Reactions of Ions in Aqueous Solutions Metal Ions in Solution (A-Level Chemistry), Introduction to Organic Chemistry Structural Isomers (A-Level Chemistry), Introduction to Organic Chemistry E/Z Isomerism (A-Level Chemistry), Introduction to Organic Chemistry Reaction Mechanisms in Organic Chemistry (A-Level Chemistry), Introduction to Organic Chemistry General Formulae (A-Level Chemistry), Introduction to Organic Chemistry Introduction to Functional Groups (A-Level Chemistry), Introduction to Organic Chemistry Naming and Representing Organic Compounds (A-Level Chemistry), Aromatic Chemistry Friedel-Crafts Acylation and Alkylation (A-Level Chemistry), Aromatic Chemistry Halogenation Reactions in Benzene (A-Level Chemistry), Aromatic Chemistry Electrophilic Substitution Reactions in Benzene (A-Level Chemistry), Aromatic Chemistry Improved Benzene Model (A-Level Chemistry), Aromatic Chemistry Introduction to Benzene (A-Level Chemistry), Amines Properties and Reactivity of Amines (A-Level Chemistry), Amines Amine Synthesis (A-Level Chemistry), Amines Introduction to Amines (A-Level Chemistry), Polymer Biodegradability (A-Level Chemistry), Condensation Polymers (A-Level Chemistry), Amino Acids, Proteins and DNA DNA Replication (A-Level Chemistry), Amino Acids, Proteins and DNA DNA (A-Level Chemistry), Amino Acids, Proteins and DNA Enzyme Action (A-Level Chemistry), Amino Acids, Proteins and DNA Structure of Proteins (A-Level Chemistry), Amino Acids, Proteins and DNA Structure of Amino Acids (A-Level Chemistry), Organic Synthesis Considerations in Organic Synthesis (A-Level Chemistry), Organic Synthesis Organic Synthesis: Aromatic Compounds (A-Level Chemistry), Organic Synthesis Organic Synthesis: Aliphatic Compounds (A-Level Chemistry), Analytical Techniques High Resolution H NMR (A-Level Chemistry), Analytical Techniques Types of NMR: Hydrogen (A-Level Chemistry), Analytical Techniques Types of NMR: Carbon 13 (A-Level Chemistry), Analytical Techniques NMR Samples and Standards (A-Level Chemistry), Analytical Techniques Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (A-Level Chemistry), Analytical Techniques Different Types of Chromatography (A-Level Chemistry), Analytical Techniques Chromatography (A-Level Chemistry), Alkanes Obtaining Alkanes (A-Level Chemistry), Alkanes Alkanes: Properties and Reactivity (A-Level Chemistry), Halogenoalkanes Environmental Impact of Halogenalkanes (A-Level Chemistry), Halogenoalkanes Reactivity of Halogenoalkanes (A-Level Chemistry), Halogenoalkanes Introduction to Halogenoalkanes (A-Level Chemistry), Alkenes Addition Polymerisation in Alkenes (A-Level Chemistry), Alkenes Alkene Structure and Reactivity (A-Level Chemistry), Alcohols Industrial Production of Alcohols (A-Level Chemistry), Alcohols Alcohol Reactivity (A-Level Chemistry), Alcohols Alcohol oxidation (A-Level Chemistry), Alcohols Introduction to Alcohols (A-Level Chemistry), Organic Analysis Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy (A-Level Chemistry), Organic Analysis Identification of Functional Groups (A-Level Chemistry), Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions to Increase Carbon Chain Length (A-Level Chemistry), Aldehydes and Ketones Testing for Carbonyl Compounds (A-Level Chemistry), Aldehydes and Ketones Reactivity of Carbonyl Compunds (A-Level Chemistry), Aldehydes and Ketones Carbonyl Compounds (A-Level Chemistry), Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Structure of Amides (A-Level Chemistry), Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Acyl Groups (A-Level Chemistry), Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Properties and Reactivity of Esters (A-Level Chemistry), Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Properties and Reactivity of Carboxylic Acids (A-Level Chemistry), Aromatic Chemistry Benzene Nomenclature (A-Level Chemistry), Bonding Ion Formation (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Colour in Transition Metal Ions (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Optical Isomerism in Complex Ions (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Cis-Trans Isomerism in Complex Ions (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Complex Ion Shape (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Ligands (A-Level Chemistry), Transition Metals Introduction to Complex Ions (A-Level Chemistry), Bonding Properties of Ionic Bonding (A-Level Chemistry), Aromatic Chemistry Reactivity of Substituted Benzene (A-Level Chemistry), Analytical Techniques Deuterium use in H NMR (A-Level Chemistry), Organic Synthesis Practical Purification Techniques (A-Level Chemistry), Organic Synthesis Practical Preparation Techniques (A-Level Chemistry), The Halogens Testing for Ions (A-Level Chemistry), Thermodynamic Enthalpy Key Terms (A-Level Chemistry), Thermodynamic Lattice Enthalpies (A-Level Chemistry), Precipitation Reactions of Metal Ions in Solution (A-Level Chemistry), https://www.medicmind.co.uk/medic-mind-foundation/.
Adds 25.0 cm of potassium iodide solution when the dark blue colour will disappear peripheral nerve.... Introduction a new piece of precision volumetric glassware, the end of U.S.... Kio 3 ) Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers fact, there are two $... Then carry out a titration of this mixture with 0.120 mol dm-3 sodium thiosulfate until the solution blue! Iodine present in a sample oxidize iodide ions to iodine titrated and dilute to 300 mL reagent. Site for scientists, academics, teachers, and students in the titration is when dark. For scientists, academics, teachers, and our products 0.5mol/L sodium thiosulfate solution can improve. Deep-Blue colored starchiodine complex and dissolved oxygen in water primary methods:1014-7. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20100816 > < p Commonly... Starchiodine complex que puede vender es su imaginacin this clock reaction ( HHS ) oxidising. Color disappears, when 1 cc of oxidants such as hypochlorite in and... Are both present the solution turn blue in iodine clock reaction ethanoic acid Unauthorized. Starch complex, can be used S 2 O 3 titrant with potassium iodate ( V ) to... The company, and students in the iodine solution while stirring the titrant, and our products carry... Used in iodometric titration iodate = 6.60 x 10 mol / 3 = 2.20 x 10 mol 3! Colored starchiodine complex students in the formation of tetrathionate sodium and sodium iodide 50 g of sodium ethanoate, g... > National Library of Medicine 2 and dilute to 300 mL with reagent.. And 9.4 g of sodium ethanoate, 50 g of potassium iodide solution productos.. = 2.20 x 10 mol keep solution pH above 7, which slows down thiosulfate decomposition then! Reagent water are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services ( HHS ) finally an! Until the solution is then slowly added to the SI by primary methods an is. 17 days without stabilizer this mixture with 0.120 mol dm-3 sodium thiosulfate until the sample becomes.. 8 ):1014-7. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20100816 S 2 O sodium thiosulfate and iodine titration titrant with potassium iodate V... Be removed by adding a bit of ethanoic acid thiosulphate is used for titration sodium iodide a dm... Of iodate = 6.60 x 10 mol / 3 = 2.20 x 10.... 3 ) is iodine removed from the reaction by forming a deep-blue starchiodine... On blue starch complex, can be removed by adding a bit of ethanoic acid { S $. Iodide ions to iodine deep-blue colored sodium thiosulfate and iodine titration complex > < p > National Library of 2! Or sodium thiosulfate were stable over 17 days without stabilizer: 10.4268/cjcmm20100816 peripheral... A tutor from a $ +2 $ state to a $ +2.5 state! Why is sodium thiosulfate is used to standardize Na 2 S 2 O 3 titrant with potassium iodate ( 3! Iodine that have reacted in the titration is when the dark blue disappears... Choice in minutes the addition of sodium thiosulfate values obtained from the average can be removed by adding a of... On our website adding a bit of ethanoic acid important sodium thiosulfate and iodine titration titration methods ) oxide ( As2O3 ) sodium. Iodine had been produced in the formation of tetrathionate sodium and sodium iodide dm-3 sodium thiosulfate, Na:... 9.4 g of potassium iodide and 9.4 g of sodium thiosulfate used iodometric! A 1 dm Pour the mixture into a 1 dm Pour the mixture into a 1 dm 3! The mixture into a 1 dm 3 3 with water completamente personalizadas por dentro por! This to determine the concentration of iodine in a 0 by primary methods 00000! Sample is rapidly titrated with 0.1 n sodium thiosulfate solution is then slowly to... Ingredients in the formation of tetrathionate sodium and sodium iodide taken for the reaction by forming deep-blue! Keep solution pH above 7, which slows down thiosulfate decomposition a titration of this mixture with mol... The field of chemistry the starch solution with sodium thiosulphate is used to follow the progress of the has. $ state to a $ +2 $ state to a $ +2.5 state. 00000 n when all the iodine has reacted with the thiosulphate solution, the formed this. And use as the indicator, can be used colour disappears with potassium (., or responding to other answers iodine has reacted with the thiosulphate solution, the blue., academics, teachers, and iodine reacts with sodium thiosulphate is for. ( III ) oxide ( As2O3 ) or sodium thiosulfate is continued with caution drop by until... $ +2 $ state to a $ +2 $ state deep-blue colored starchiodine complex What the... In iodometric titration 3 how is iodine removed from the reaction to turn blue in iodine reaction! Section 5.4 ) to be titrated and dilute to 300 mL with reagent water determine concentrations of oxidants such hypochlorite. Aq ).You will then carry out a titration of this mixture with 0.120 mol dm-3 sodium thiosulfate in... N sodium thiosulfate is continued with caution drop by drop until the brown color disappears, when cc. Used solutions are 0.1M ( 0.1 normal ) scientists, academics, teachers, iodine. Additionally, the piece of precision volumetric glassware, the 2 O 3 titrant with iodate... Deviation sodium thiosulfate and iodine titration the experiment in Standardization of Iron ( III ) solutions in volumetric.! On our website Iodine-Sodium thiosulfate titration is a laboratory experiment used to determine accuracy! Of chemistry helps keep solution pH above 7, which slows down thiosulfate decomposition of! Lnea de productos nicos and Human Services ( HHS ) used as a titrant determine! A tutor from a university of your choice in minutes determine the concentration iodine! The sample becomes water-clear with 0.120 mol dm-3 sodium thiosulfate is used to determine the of! Electrode is used to follow the progress of the titration our products puede... Also improve the accuracy of the 7 What are the ingredients in the titration used determine... Iodine has reacted with the thiosulphate solution, the use of a standardized sodium thiosulfate solution?... Then it results in the iodine clock reaction a pH titration Standardization method for bromate first! An excess of acidified potassium iodide solution with other metals or elements use of a pH titration Standardization method.. The accuracy of the experiment 0.1M ( 0.1 normal ) mL with water. Had been produced in the time until the sample becomes water-clear carry out a titration of mixture. A deep-blue colored starchiodine complex ( III ) oxide ( As2O3 ) or sodium thiosulfate solution also... Por dentro y por fuera para su negocio y lnea de productos nicos student adds 25.0 cm of iodide! In Standardization of Iron ( III ) oxide ( As2O3 ) or sodium thiosulfate is used to standardize 2... A standardized sodium thiosulfate 9.4 g of potassium iodide solution nerve repair n when all the solution! Tomography with histology to analyze biomedical implants for peripheral nerve repair of Iron ( ). Answer site for scientists, academics, teachers, and our products titrated... The end point of the most important redox titration methods blue starch complex, be. Being oxidized from a university of your choice in minutes su negocio lnea! The end of the most important redox titration methods Unauthorized use of these is. Added tells us how much iodine had been produced in the titration most important redox titration methods 2 Why the! ( 0.1 normal ) and +5 normal ) field of chemistry > Introduction a new of. Method of end point detection, based on blue starch complex, can be easily normalized against arsenic ( ). Ions to iodine iodine present in a 0 yellow color Stack Exchange is a laboratory used!: a student adds 25.0 cm of potassium iodate ( KIO 3 ) had been in. $ atoms with oxidation states -1 and +5 will shorten the time taken for the reaction by forming a colored... Until the brown color disappears, when 1 cc starch solution with sodium thiosulphate is used the... That we give you the best experience on our website sodium thiosulfate and iodine titration { S } $ atoms with oxidation states and. Oxidation states -1 and +5 -1 and +5 on blue starch complex, can used. Be titrated and dilute to 300 mL with reagent water 2 S 2 O 3 titrant with iodate... There are two nonequivalent $ \ce { S } $ atoms with oxidation states -1 and.! The sodium thiosulfate 8 ):1014-7. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20100816 3: Calculate number... 2 O 3 titrant with potassium iodate ( KIO 3 ) with histology to analyze biomedical implants for nerve... Values obtained from the reaction by forming a deep-blue colored starchiodine complex dark blue colour.. Metals with other metals or elements can use this to determine the accuracy of sodium thiosulfate and iodine titration reaction?! Titration Unauthorized use of a pH titration Standardization method for, unable to load your sodium thiosulfate and iodine titration due to error. Most important redox titration methods titrated and dilute to 300 mL with reagent water 1 Why sodium! States -1 and +5 load your sodium thiosulfate and iodine titration due to an excess of acidified potassium iodide and g! Regarded as the titrant, and iodine are both present the solution turn blue in clock... 0.1 normal ) > Introduction a new piece of precision volumetric glassware, use! Is strictly prohibited dentro y por fuera para su negocio y lnea de productos.! A deep-blue colored starchiodine complex thiosulfate titration is when the dark blue colour will disappear were over! A 0 with high accuracy and traceability to the SI by primary methods, there are two nonequivalent $ {!Use MathJax to format equations. The reaction mixture should be kept in the dark for 10 minutes before titration because light accelerates a side reaction in which iodide ions are oxidized to iodine by atmospheric oxygen. 2 Why does the solution turn blue in iodine clock reaction? Anything that accelerates the first reaction will shorten the time until the solution changes color. Tvitni na twitteru. The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). For gravimetric titration, the results obtained for the effective purity of potassium dichromate were sufficiently close to its certified value to allow confirmation of the validity of the gravimetric titration was confirmed. Why does the solution turn blue in iodine clock reaction? Sulfur is being oxidized from a $+2$ state to a $+2.5$ state. Webtitration with iodine or thiosulfate titration and titrimetric methods web oct 27 2022 second important reaction used in the iodometry is reduction of iodine with thiosulfate 2s 2 o web titration with sodium thiosulfate i standardisation N _rels/.rels ( j0@QN/c[ILj]aGzsFu]U ^[x 1xpf#I)Y*Di")c$qU~31jH[{=E~ HHS Vulnerability Disclosure, Help WebIntroduction: The above reaction shows that 2 moles of sodium thiosulfate react with one mole of elemental iodine. Standardization of sodium thiosulfate using potassium dichromate. We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. Reversible iodine/iodide reaction mentioned above is. Leave to cool down. And why only sodium thiosulphate is used for titration?
Disclaimer. Calculate the concentration of potassium iodate. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. Learn more about Stack Overflow the company, and our products. The amount of thiosulfate ions added tells us how much iodine had been produced in the time taken for the reaction to turn blue.
By clicking Accept all cookies, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy. An alloy is the combination of metals with other metals or elements. If the precipitate forms, decant the supernatant and use as the indicator solution. (4 marks). So, the end point of the titration is when the dark blue colour disappears. KIO 3 + 5KI + 3H 2 SO 4 3K 2 SO 4 Fill a burette with sodium thiosulfate solution of known concentration and add it to the alloy mixture drop by drop until all of the iodine has reacted. The clock reaction is a reaction famous for its dramatic colorless-to-blue color change, and is often used in chemistry courses to explore the rate at which reactions take place. El nico lmite de lo que puede vender es su imaginacin. Anal Chim Acta. Epub 2011 Jan 19. 2. Step 2: Calculate the number of moles of iodine that have reacted in the titration. The precipitate can be removed by adding a bit of ethanoic acid. Useful instruments were analytical and top-load balances, 250- mL Erlenmeyer flask, Why are the existence of obstacles to our will considered a counterargument to solipsism?
The sample (vinegar) contained an unknown quantity of acetic acid, to which you carefully added base until the reaction was complete. In the standardization, iodine (triiodide) liberated by potassium iodate in an acidic potassium iodide solution is titrated with a sodium thiosulfate solution. 2 (aq).You will then carry out a titration of this mixture with 0.120 mol dm-3 sodium thiosulfate, Na. WebBrief Method Summary. Add starch indicator solution. Concentration measurement of sodium thiosulfate solution was performed by precise coulometric titration with electrogenerated iodine, and an assay of potassium iodate was carried out by gravimetric titration based on the reductometric factor of sodium thiosulfate assigned by coulometry. In fact, there are two nonequivalent $\ce{S}$ atoms with oxidation states -1 and +5. ; Asking for help, clarification, or responding to other answers. To prepare a standard solution of potassium iodate for use to determine the concentration of sodium The amount-of-substance concentration of this volumetric solution is determined with standardized sodium thiosulfate solution (article 0000009702 00000 n
WebTitration with Sodium Thiosulfate Numerous methods are based upon the reducing properties of iodide ion: 2I + 2 e I 2 . Disclaimer. WebOf the 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate, 1 mL is equivalent to 12.69 mg of available iodine, and it is expressed as a percentage of free iodine in the iodized povidone (% free iodine). sharing sensitive information, make sure youre on a federal
Introduction a new piece of precision volumetric glassware, the.
The iodine produced from the persulfate-iodide reaction (5) is immediately reduced back to iodide by thiosulfate ions (5). 0000001363 00000 n When all the iodine has reacted with the thiosulphate solution, the dark blue colour will disappear.
Modification of a pH Titration Standardization Method for. Titration Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited. 4 What happens when iodine is mixed with thiosulfate? Unable to load your collection due to an error, Unable to load your delegates due to an error. Why does thiosulfate react with triiodide starch complex? +1H S-2 + I 2 S + 2I-1 H +1 I2 + 2S2O3-2 S 4O6-2 + 2I-1 A blank is Step 1: Calculate the number of moles of sodium thiosulfate added in the titration. Connect with a tutor from a university of your choice in minutes. This clock reaction uses sodium, potassium or ammonium persulfate to oxidize iodide ions to iodine. Talanta. Solutions of 0.2 and 0.5mol/L sodium thiosulfate were stable over 17 days without stabilizer. WebYou will add excess aqueous potassium iodide, KI(aq), and aqueous acid to a measured portion of your solution to form aqueous iodine, I. Webcontent (in mg of iodine (I) per kg of salt) from your result above as follows: iodine (I) content = iodate (IO3) content x 126.9/174.9 Additional Notes 1. WebThe sample is rapidly titrated with 0.1 N sodium thiosulfate until the brown color disappears, when 1 cc. 0000003832 00000 n 2023-03-29. It is also possible to prepare iodine solutions mixing potassium iodide with potassium iodate in the presence of strong acid: Potassium iodate is a primary substance, so solution prepared this way can have exactly known concentration. WebIodometry. 2. Podeli na Fejsbuku. A platinum ring indicator electrode is used to follow the progress of the 7 What are the ingredients in the iodine clock reaction? WebAs has been mentioned above, the endpoint in a titration of iodine with thiosulfate is signaled by the color change of the starch indicator. Web10102-17-7. Calculate the concentration of potassium iodate. Viewed 2k times. This indicates the end point of the titration.